Salaried tax payers|Capital gain taxation|House property income|Future & options|




“Tax2return specializes in offering a wide range of financial services tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses and individuals. Our expertise includes GST services, accounting solutions, taxation consultancy, and efficient tax filing. With a commitment to accuracy, compliance, and client satisfaction, we strive to empower our clients with comprehensive financial support, helping them navigate regulatory requirements and achieve their financial goals effectively.”
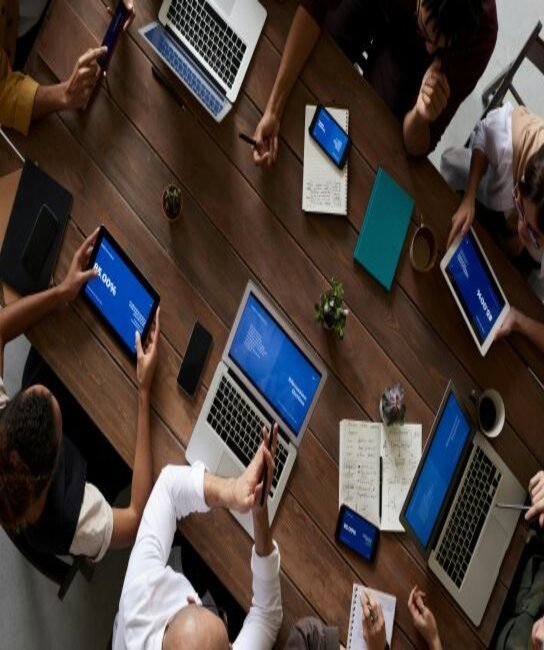


"At tax2return, our mission is to provide comprehensive support and expertise in taxation, GST, and accounting services. We are dedicated to simplifying financial complexities for our clients, ensuring compliance, and fostering long-term success through trusted guidance and innovative solutions."

.Our company boasts a highly skilled and professional team dedicated to delivering expert services in GST, accounting, taxation, and financial consultancy

client data is our top priority. We employ state-of-the-art security measures to protect all sensitive information entrusted to us.so dont worry about security
We understand the critical importance of timely tax filing and other financial services. Our dedicated team works diligently to ensure all deadlines are accurately

seamless services that streamline your financial processes. From GST and taxation to comprehensive accounting solutions, our goal is to provide you with a hassle-free experience.
Unburden yourself from financial complexities. Our tax experts offer personalized guidance for all your accounting and income tax needs.
Never miss a deadline again. We prioritize on-time filing and meticulously review your information to ensure accurate tax returns, maximizing your refund or minimizing your tax burden.
Our user-friendly platform makes filing your taxes a breeze. Say goodbye to paperwork! We simplify data collection and streamline the entire process for a stress-free experience.
We don't offer a one-size-fits-all approach. We take the time to understand your unique tax situation and answer any questions you may have, ensuring you feel confident throughout the process.
Knowing your taxes are handled by experts allows you to breathe easy. We'll handle the details with efficiency and accuracy, so you can focus on what matters most to you.
An Income Tax Return (ITR) is a document you file with the tax department to report your income earned and taxes paid during a financial year. It helps the government determine if you owe any additional taxes or are eligible for a refund.
Here are some important documents to gather for ITR filing:
Tax planning isn’t just about filling out forms at the last minute. It’s a proactive strategy to minimize your tax burden and maximize your potential tax refund. Here’s how it can benefit you:
Here are some key aspects of effective tax planning:
An income tax notice from the Income Tax Department (ITD) of India can be a cause for concern, but it’s important to stay calm and understand what it means. Here’s a breakdown:
Benefits of GST:
GST registration and filing requirements vary depending on your business type and turnover. Here’s a general list of documents you might need:
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a mechanism where a tax is collected at the source of income by the deductor (payer) and deposited to the government on behalf of the deductee (payee). TDS return filing is the process of reporting this deducted tax to the Income Tax Department (ITD).
For Deductors (Those who deduct TDS):
For Deductees (Those whose TDS is deducted):
While deductees (like employees or those receiving rent) don’t directly file TDS returns, they do need some documents for their own tax filing:
A TAN (Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number) is a crucial element for businesses in India that deduct tax at source (TDS) from certain payments. It acts as your identification number for TDS purposes, allowing you to collect and deposit tax to the government on behalf of others.
Documents Required for TAN Registration:
Important Points to Remember:
Accounting is the system of recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and reporting financial information about a business. It’s like a language that translates financial transactions into a clear and understandable story about a company’s performance.
The Accounting Process:
Types of Accounting:
An income tax return (ITR) is a form used to
declare your income, expenses, tax deductions, and investments to the government. It helps in
calculating your tax liability and paying any due taxes or claiming refunds.
Individuals, HUFs, companies, and other
entities like Body corporates, Trust, etc. earning income above the basic exemption limit
specified by the Income Tax Department need to file an ITR. Which is 2,50,000/3,00,000 for old
and New Scheme
There are various ITR forms like ITR-1
(Sahaj), ITR-2, ITR-3, ITR-4 (Sugam), etc., each meant for different types of taxpayers and
income sources.
ITR 1 : This return is applicable for a Resident (other than Not Ordinarily Resident) Individual
having Total Income from any of the following sources up to ₹ 50 lakh. Source of Income is
Salary/pension, One House Property, Other Sources Income basically Interest, family pension,
Gaming etc. Agriculture income upto Rs. 5,000/-
ITR 1 cant be filed by a person who :
(a) is a Director in a company
(b) has held any unlisted equity shares at any time during the previous year
(c) has any asset (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India
(d) has signing authority in any account located outside India
(e) has income from any source outside India
(f) is a person in whose case tax has been deducted u/s 194N
(g) is a person in whose case payment or deduction of tax has been deferred on ESOP
(h) has any brought forward loss or loss to be carried forward under any head of income (i) has
total income exceeding Rs. 50 lakhs.
ITR 2 : This return is applicable for Individual and Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) who is not
having income from business & Profession and also who is not eligible to file the ITR 1. Mainly
this return form is applicable when Assessee is having capital gain (Shares of Indian and foreign
company) income and having more than 50 lakh income and also having more than 1 house
property.
ITR 3 : This return is applicable for Individual and Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) having
income from Business and Profession and who is not eligible for ITR 1,2 and 4.
ITR 4 : This return is applicable for an Individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), who is
Resident other than Not Ordinarily Resident or a Firm (other than LLP) which is a Resident
having Total Income up to ₹ 50 lakh and having income from Business or Profession which is
computed on a presumptive basis (u/s 44AD / 44ADA / 44AE) and income from any of the
following sources: Source of Income is Salary/pension, One House Property, Other Sources
Income basically Interest, family pension, Gaming etc. Agriculture income upto Rs. 5,000/-
The due date for individuals is
usually July 31st of the assessment year. For businesses and entities requiring audit, the due date
is typically September 30th.
You can file your ITR online through the
Income Tax Department's e-filing portal. You'll need to register, fill in the necessary details,
upload documents, and submit the return
Common documents include
Form 16, salary slips, interest certificates, investment proofs, bank statements, and TDS
certificates.
Yes, if you discover any errors in your filed
ITR, you can file a revised return within the time allowed under the Income Tax Act.
Common deductions include Section
80C (investments), 80D (medical insurance), 80G (donations), and 24(b) (home loan interest).
You can claim deductions up to
Rs 1.5 lakh under Section 80C for investments in PPF, NSC, ELSS, LIC premiums, and other
specified instruments.
You can check your refund
status on the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal or the NSDL website by providing your
PAN and assessment year details.
Penalties for late filing
include a fee of Rs 5,000 if filed after the due date but before December 31st, and Rs 10,000 if
filed later. For small taxpayers with income up to Rs 5 lakh, the maximum penalty is Rs 1,000.
If you receive an income tax
notice, carefully read it to understand the reason and respond within the specified time frame.
You may need to provide additional documents or clarifications.
Double-check all personal
and financial details, ensure accurate reporting of income and deductions, and verify tax credits.
Use reliable software or consult a tax professional if needed.
Beyond compliance, we optimize.

Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us
Let’s Start with us